1. 写在前面
mprotect是一种Linux提供的内存保护的系统调用,通过修改内存区的读、写、执行等属性限制内存访问的方式,若非法访问内存区,则进程会发出SIGSEGV信号。mprotect可用于捕捉内存访问行为。
2. mprotect用法
Linux manual page提供mprotect用法,形式:
#include <sys/mman.h>
int mprotect(void *addr, size_t len, int prot);
mprotect保护[addr, addr+len-1]区域的内存页,addr需要页对齐。
内存属性:
- PROT_NONE: 内存不可访问;
- PROT_READ: 内存可读;
- PROT_WRITE: 内存可写;
- PROT_EXEC: 内存可执行;
- PROT_SEM: 内存可原子操作;
- PROT_SAO: 内存必须有序处理请求;
- …
提供的例程:
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#define handle_error(msg) \
do { perror(msg); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); } while (0)
static char *buffer;
static void
handler(int sig, siginfo_t *si, void *unused)
{
/* Note: calling printf() from a signal handler is not safe
(and should not be done in production programs), since
printf() is not async-signal-safe; see signal-safety(7).
Nevertheless, we use printf() here as a simple way of
showing that the handler was called. */
printf("Got SIGSEGV at address: %p\n", si->si_addr);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int
main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int pagesize;
struct sigaction sa;
sa.sa_flags = SA_SIGINFO;
sigemptyset(&sa.sa_mask);
sa.sa_sigaction = handler;
if (sigaction(SIGSEGV, &sa, NULL) == -1)
handle_error("sigaction");
pagesize = sysconf(_SC_PAGE_SIZE);
if (pagesize == -1)
handle_error("sysconf");
/* Allocate a buffer aligned on a page boundary;
initial protection is PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE. */
buffer = memalign(pagesize, 4 * pagesize);
if (buffer == NULL)
handle_error("memalign");
printf("Start of region: %p\n", buffer);
if (mprotect(buffer + pagesize * 2, pagesize,
PROT_READ) == -1)
handle_error("mprotect");
for (char *p = buffer ; ; )
*(p++) = 'a';
printf("Loop completed\n"); /* Should never happen */
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
}
3. mprotect源码分析
按照下面线索追踪系统调用mprotect在内核中的执行过程:
SYSCALL_DEFINE3(mprotect, .., start, .., len, .., prot)
-> do_mprotect_pkey(start, len, prot, pkey=-1)
-> mprotect_fixup(vma, .., start, end, newflags)
-> change_protection(vma, start, end, newprot, cp_flags)
-> change_protection_range(vma, addr, end, newprot, cp_flags)
-> change_p4d_range(vma, pgd, add, end, newprot, cp_flags)
-> change_pmd_range(vma, pud, addr, end, newprot, cp_flags)
-> change_pte_range(vma, pmd, addr, end, newprot, cp_flags)
3.1. 页表寻址
Linux虚拟内存三级页表寻址,其中:
- PGD: page global directory
- PMD: page middle directory
- PTE: page table entry
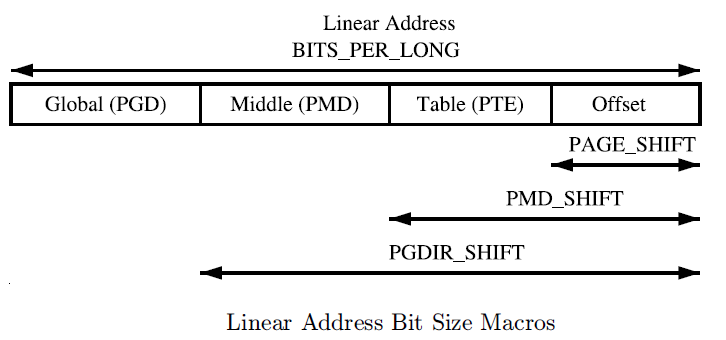
虚拟地址利用3级页表访问物理内存:
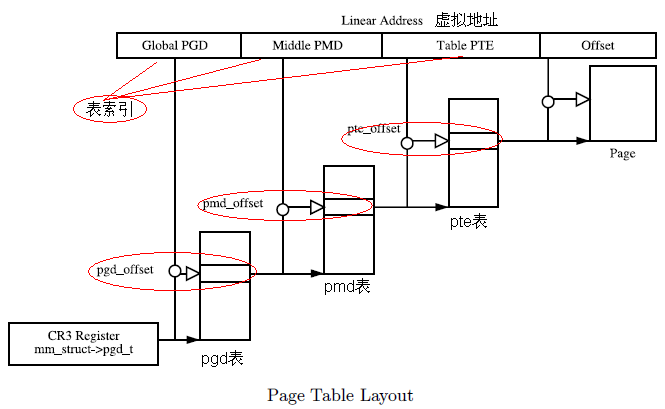
3.2. 数据结构
3.2.1. struct vm_area_struct
记录某个Task的一段虚拟内存,而Task的虚拟内存由struct mm_struct *vm_mm记录,而vm_mm的每个分段的虚拟内存vma由双向链表(vm_next和vm_prev)和红黑树管理(rb_node vm_rb)。
struct vm_area_struct {
/* The first cache line has the info for VMA tree walking. */
unsigned long vm_start; /* Our start address within vm_mm. */
unsigned long vm_end; /* The first byte after our end address
within vm_mm. */
//
/* linked list of VM areas per task, sorted by address */
struct vm_area_struct *vm_next, *vm_prev;
struct rb_node vm_rb;
/*
* Largest free memory gap in bytes to the left of this VMA.
* Either between this VMA and vma->vm_prev, or between one of the
* VMAs below us in the VMA rbtree and its ->vm_prev. This helps
* get_unmapped_area find a free area of the right size.
*/
unsigned long rb_subtree_gap;
/* Second cache line starts here. */
struct mm_struct *vm_mm; /* The address space we belong to. */
/*
* Access permissions of this VMA.
* See vmf_insert_mixed_prot() for discussion.
*/
pgprot_t vm_page_prot;
unsigned long vm_flags;
....
const struct vm_operations_struct *vm_ops; // 与这个结构结构体相关的操作,一般在模块初始化时执行自定义的ops
4. 分析调用路径源码
4.1. do_mprotect_pkey
- 根据起始地址
start找到对应的vma; - 判断vma的范围是否覆盖
start,并尝试在current task的虚拟地址空间的中找链表的前一个内存片段; - 遍历
start至end内存片段,修改内存属性。
static int do_mprotect_pkey(unsigned long start, size_t len,
unsigned long prot, int pkey)
{
unsigned long nstart, end, tmp, reqprot;
struct vm_area_struct *vma, *prev;
int error = -EINVAL;
...
vma = find_vma(current->mm, start);
error = -ENOMEM;
if (!vma)
goto out;
prev = vma->vm_prev;
...
if (vma->vm_start > start)
goto out;
...
}
if (start > vma->vm_start)
prev = vma;
for (nstart = start ; ; ) {
unsigned long mask_off_old_flags;
unsigned long newflags;
int new_vma_pkey;
/* Here we know that vma->vm_start <= nstart < vma->vm_end. */
/* Does the application expect PROT_READ to imply PROT_EXEC */
if (rier && (vma->vm_flags & VM_MAYEXEC))
prot |= PROT_EXEC;
/*
* Each mprotect() call explicitly passes r/w/x permissions.
* If a permission is not passed to mprotect(), it must be
* cleared from the VMA.
*/
mask_off_old_flags = VM_READ | VM_WRITE | VM_EXEC |
VM_FLAGS_CLEAR;
new_vma_pkey = arch_override_mprotect_pkey(vma, prot, pkey);
newflags = calc_vm_prot_bits(prot, new_vma_pkey);
newflags |= (vma->vm_flags & ~mask_off_old_flags);
/* newflags >> 4 shift VM_MAY% in place of VM_% */
if ((newflags & ~(newflags >> 4)) & VM_ACCESS_FLAGS) {
error = -EACCES;
goto out;
}
...
tmp = vma->vm_end;
if (tmp > end)
tmp = end;
if (vma->vm_ops && vma->vm_ops->mprotect) {
error = vma->vm_ops->mprotect(vma, nstart, tmp, newflags);
if (error)
goto out;
}
error = mprotect_fixup(vma, &prev, nstart, tmp, newflags);
if (error)
goto out;
nstart = tmp;
if (nstart < prev->vm_end)
nstart = prev->vm_end;
if (nstart >= end)
goto out;
vma = prev->vm_next;
if (!vma || vma->vm_start != nstart) {
error = -ENOMEM;
goto out;
}
prot = reqprot;
}
out:
mmap_write_unlock(current->mm);
return error;
}
4.2. mprotect_fixup
- 尝试与vma链表上的前向和后向vma合并;
- 改变vma对应
[start, end]内存页属性。
int
mprotect_fixup(struct vm_area_struct *vma, struct vm_area_struct **pprev,
unsigned long start, unsigned long end, unsigned long newflags)
{
struct mm_struct *mm = vma->vm_mm;
unsigned long oldflags = vma->vm_flags;
long nrpages = (end - start) >> PAGE_SHIFT;
unsigned long charged = 0;
pgoff_t pgoff;
int error;
int dirty_accountable = 0;
if (newflags == oldflags) {
*pprev = vma;
return 0;
}
...
/*
* First try to merge with previous and/or next vma.
*/
pgoff = vma->vm_pgoff + ((start - vma->vm_start) >> PAGE_SHIFT);
*pprev = vma_merge(mm, *pprev, start, end, newflags,
vma->anon_vma, vma->vm_file, pgoff, vma_policy(vma),
vma->vm_userfaultfd_ctx);
if (*pprev) {
vma = *pprev;
VM_WARN_ON((vma->vm_flags ^ newflags) & ~VM_SOFTDIRTY);
goto success;
}
*pprev = vma;
if (start != vma->vm_start) {
error = split_vma(mm, vma, start, 1);
if (error)
goto fail;
}
if (end != vma->vm_end) {
error = split_vma(mm, vma, end, 0);
if (error)
goto fail;
}
success:
/*
* vm_flags and vm_page_prot are protected by the mmap_lock
* held in write mode.
*/
vma->vm_flags = newflags;
dirty_accountable = vma_wants_writenotify(vma, vma->vm_page_prot);
vma_set_page_prot(vma);
change_protection(vma, start, end, vma->vm_page_prot,
dirty_accountable ? MM_CP_DIRTY_ACCT : 0);
/*
* Private VM_LOCKED VMA becoming writable: trigger COW to avoid major
* fault on access.
*/
if ((oldflags & (VM_WRITE | VM_SHARED | VM_LOCKED)) == VM_LOCKED &&
(newflags & VM_WRITE)) {
populate_vma_page_range(vma, start, end, NULL);
}
vm_stat_account(mm, oldflags, -nrpages);
vm_stat_account(mm, newflags, nrpages);
perf_event_mmap(vma);
return 0;
fail:
vm_unacct_memory(charged);
return error;
}
4.3. change_protection
判断对HugePage页属性改变还是对普通页。
unsigned long change_protection(struct vm_area_struct *vma, unsigned long start,
unsigned long end, pgprot_t newprot,
unsigned long cp_flags)
{
unsigned long pages;
BUG_ON((cp_flags & MM_CP_UFFD_WP_ALL) == MM_CP_UFFD_WP_ALL);
if (is_vm_hugetlb_page(vma))
pages = hugetlb_change_protection(vma, start, end, newprot);
else
pages = change_protection_range(vma, start, end, newprot,
cp_flags);
return pages;
}
4.4. change_protection_range
在改变页属性之前会将CPU cache中的页表信息写回,在改变页表属性之后会写回TLB的页表映射项。
static unsigned long change_protection_range(struct vm_area_struct *vma,
unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, pgprot_t newprot,
unsigned long cp_flags)
{
struct mm_struct *mm = vma->vm_mm;
pgd_t *pgd;
unsigned long next;
unsigned long start = addr;
unsigned long pages = 0;
BUG_ON(addr >= end);
pgd = pgd_offset(mm, addr);
flush_cache_range(vma, addr, end);
inc_tlb_flush_pending(mm);
do {
next = pgd_addr_end(addr, end);
if (pgd_none_or_clear_bad(pgd))
continue;
pages += change_p4d_range(vma, pgd, addr, next, newprot,
cp_flags);
} while (pgd++, addr = next, addr != end);
/* Only flush the TLB if we actually modified any entries: */
if (pages)
flush_tlb_range(vma, start, end);
dec_tlb_flush_pending(mm);
return pages;
}
4.5. change_p4d_range / change_pud_range / change_pmd_range / change_pte_range
按照p4d->pud->pmd寻址到pte,改变页属性。
改变页属性的动作由ptent = pte_modify(oldpte, newprot);执行。
static unsigned long change_pte_range(struct vm_area_struct *vma, pmd_t *pmd,
unsigned long addr, unsigned long end, pgprot_t newprot,
unsigned long cp_flags)
{
pte_t *pte, oldpte;
spinlock_t *ptl;
unsigned long pages = 0;
int target_node = NUMA_NO_NODE;
bool dirty_accountable = cp_flags & MM_CP_DIRTY_ACCT;
bool prot_numa = cp_flags & MM_CP_PROT_NUMA;
bool uffd_wp = cp_flags & MM_CP_UFFD_WP;
bool uffd_wp_resolve = cp_flags & MM_CP_UFFD_WP_RESOLVE;
do {
oldpte = *pte;
if (pte_present(oldpte)) {
oldpte = ptep_modify_prot_start(vma, addr, pte);
ptent = pte_modify(oldpte, newprot);
if (preserve_write)
ptent = pte_mk_savedwrite(ptent);
if (uffd_wp) {
ptent = pte_wrprotect(ptent);
ptent = pte_mkuffd_wp(ptent);
} else if (uffd_wp_resolve) {
/*
* Leave the write bit to be handled
* by PF interrupt handler, then
* things like COW could be properly
* handled.
*/
ptent = pte_clear_uffd_wp(ptent);
}
/* Avoid taking write faults for known dirty pages */
if (dirty_accountable && pte_dirty(ptent) &&
(pte_soft_dirty(ptent) ||
!(vma->vm_flags & VM_SOFTDIRTY))) {
ptent = pte_mkwrite(ptent);
}
ptep_modify_prot_commit(vma, addr, pte, oldpte, ptent);
pages++;
} else if (is_swap_pte(oldpte)) {
...
}
} while (pte++, addr += PAGE_SIZE, addr != end);
arch_leave_lazy_mmu_mode();
pte_unmap_unlock(pte - 1, ptl);
return pages;
}
5. 参考资料
- http://abcdxyzk.github.io/blog/2015/06/02/kernel-mm-alloc/